By Sali Lafrenie
Picture it. Paris, 1924.
You’re at the Summer Olympic Games. And there are roughly 3,000 other athletes there with you.
What sport are you playing? Tennis? Maybe soccer? Basketball? Oh wait, is it aquatics? Athletics? No, boxing? Well, whatever it is, I bet you’re excited. You should be: Team Canada only sent 65 competitors, and this is the first time the Games are going to be broadcast live on the radio!

General view of the Stadium of Colombes at the beginning of the 1924 Olympic Games (e011783298).
Considered to be the most successful of the Modern Games, the 1924 Summer Games in Paris looked very different from the Olympics that we know and love today. For starters, there were only 17 sports included in these Games. Five sports had been dropped from the previous iteration in 1920, with others included solely for demonstration or exhibition purposes.
Playing host for a third time, Paris 2024 will see Canada send 338 athletes to compete. The Games boast a whopping 32 sports, doubling the number of sports included at the 1924 Olympics.
In honour of the centenary, let’s dive into the 1924 Olympic Games!
1924 Winter Olympics
Did you know that when France bid to host the Summer Olympics in 1924, they accidentally started a new trend? That trend was the Winter Olympic Games.
The practice of hosting the Summer and Winter Games in the same year—sometimes in the same country—continued until 1992 when the International Olympic Committee decided to shift the Games to an alternating two-year schedule.
Before 1924, the Olympics only consisted of summer sports and did not have a winter sports equivalent. But there’s always a first. Hosted in Chamonix, France from January 25 to February 5, 1924, 260 athletes competed across 16 events. This means that 2024 is also the 100-year anniversary of the first Winter Olympic Games.
While Canada only sent 12 athletes to these Games—collectively earning a singular medal—there’s more to the story than that. The Chamonix Olympics was just the beginning for these athletes and the Canadian Winter Olympic Team, which had a roster of 215 athletes in 2022.
Charles “Charlie” Gorman, New Brunswicker and First World War Veteran, was one of these athletes. He made his Olympic debut in speed skating alongside the debut of the sport itself. Despite a disappointing finish in the 1924 Games, Gorman competed and won medals for Team Canada in numerous competitions, such as the American Championships, the Canadian Championships, and the World Championships.
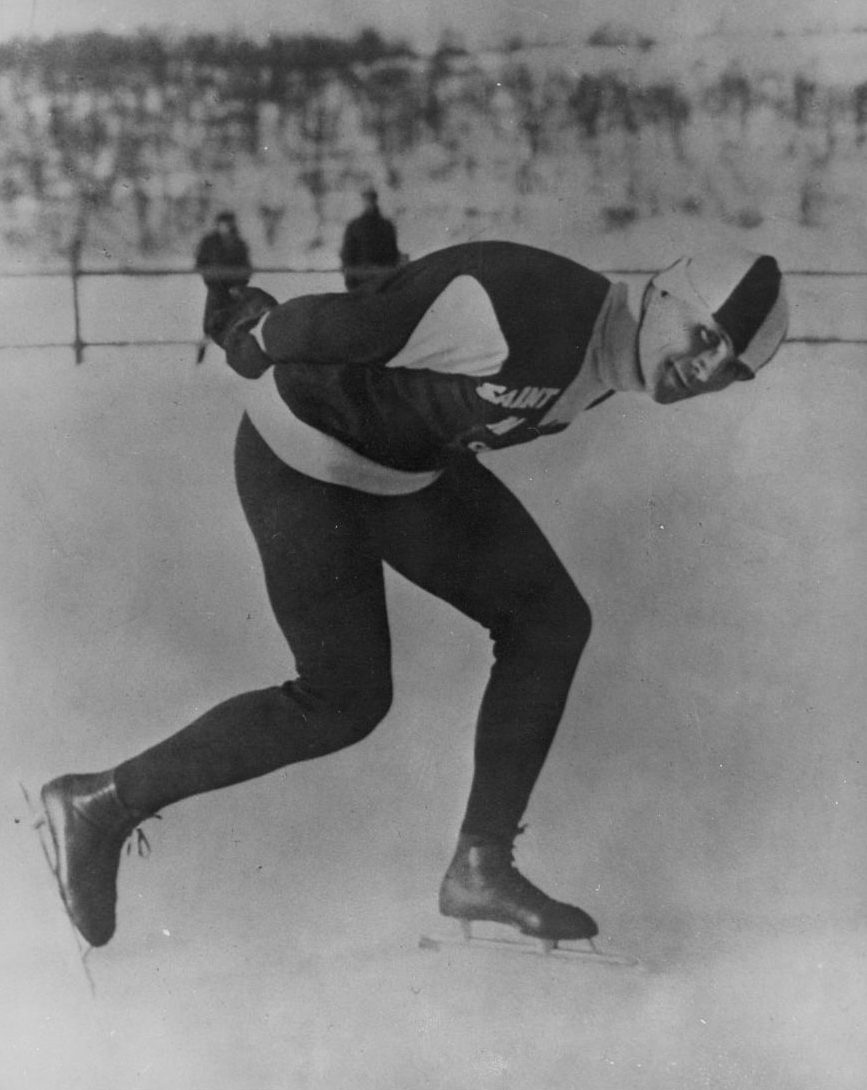

Photo of Charles Gorman speed skating (a050382).
Cecil Smith Hedstrom also made history at these Olympic Games when she became the first female Olympian to represent Canada. Competing in figure skating, Smith appeared in three Olympic Games and achieved many early feats to propel Canadian figure skating onto the world stage. For all these reasons and more, Smith was inducted into the Skate Canada Hall of Fame in 1991.
Earning the only medal for Team Canada at the Chamonix Games, the Toronto Granites Hockey Club won Canada’s first Winter Olympic gold medal. With this win, the Granites extended Canada’s Olympic ice hockey medal streak, initiated in 1920 by the Winnipeg Falcons who won gold in Antwerp. While ice hockey made its debut in the Antwerp Games, that was the first and last time the sport was included in the Summer Olympics. This means that Canada is the only country to have won a gold medal in ice hockey at both the Summer and the Winter Olympic Games.
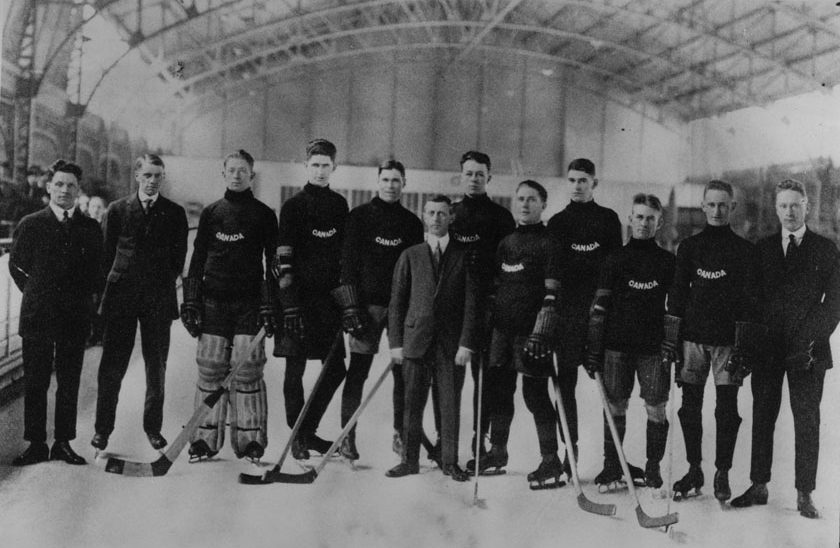

Winnipeg Falcons, Olympic Champions (a049622).
1924 Summer Olympics
While all Olympic Games are important, the 1924 Summer Games had a special glow to it: live radio transmissions, the introduction of the Athlete’s Village, and the debut of the Olympic motto, “Faster, Higher, Stronger.” The Modern Games ushered in a new era of international sports competitions that has only continued to expand in size and spectacle since 1924.
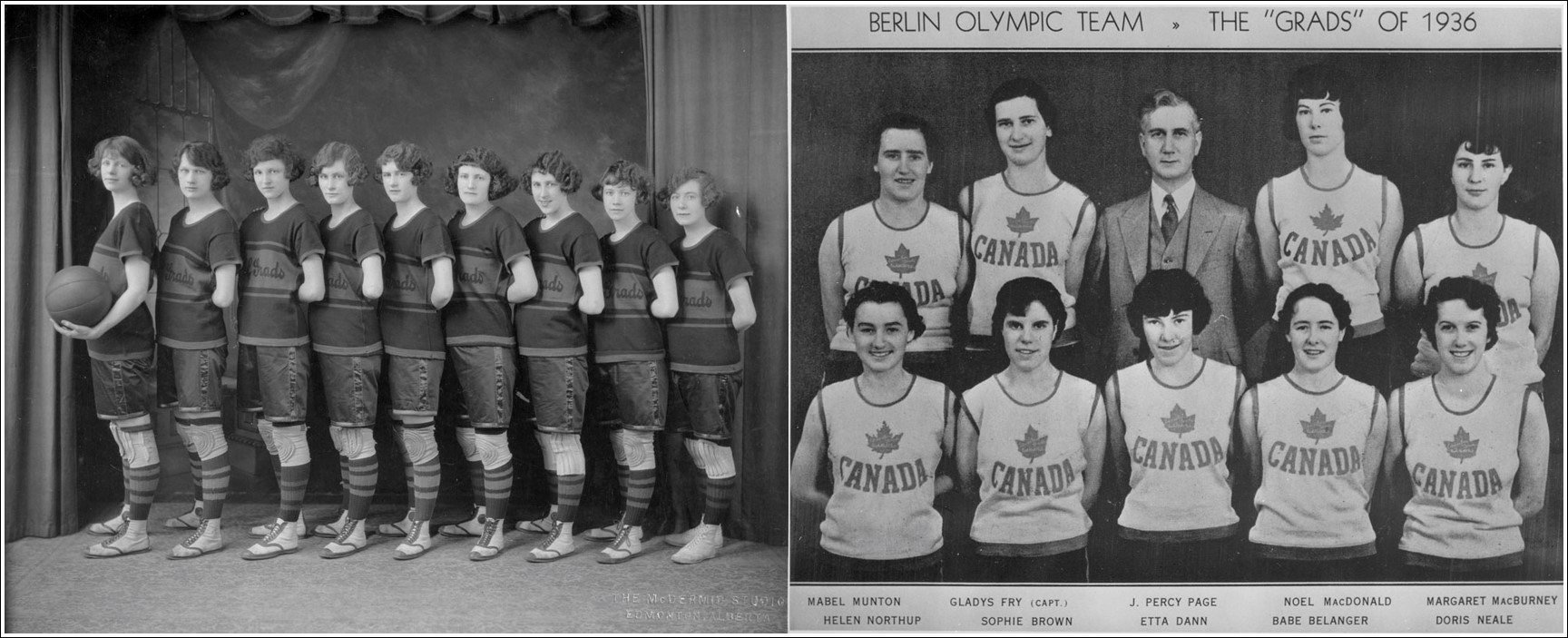
One of the greatest success stories of the 1924 Olympics comes from a group of athletes who technically were not a part of the Games: the Edmonton Grads. Although basketball was not officially included in the Olympics—men’s basketball would join in 1936 and women’s basketball would join in 1976—the Fédération sportive féminine internationale (FSFI) decided to hold their own matches alongside the Summer Games.
At home and abroad, the Grads were a difficult team to beat. They won approximately 95% of all the games they ever played and won the FSFI women’s basketball tournaments in 1924, 1928, and 1936.
Making his Olympic debut, Canadian hurdler Warren “Monty” Montabone soared onto the world stage in Paris 1924 and then again in Amsterdam 1928. In between Olympic appearances, Monty also set a Canadian record that stood for 58 years in the 110 m hurdles event. His athletic career can be traced beyond the Olympics all the way back to his time as a student athlete at Loyola and as an amateur athlete with the Montreal Amateur Athletic Association.
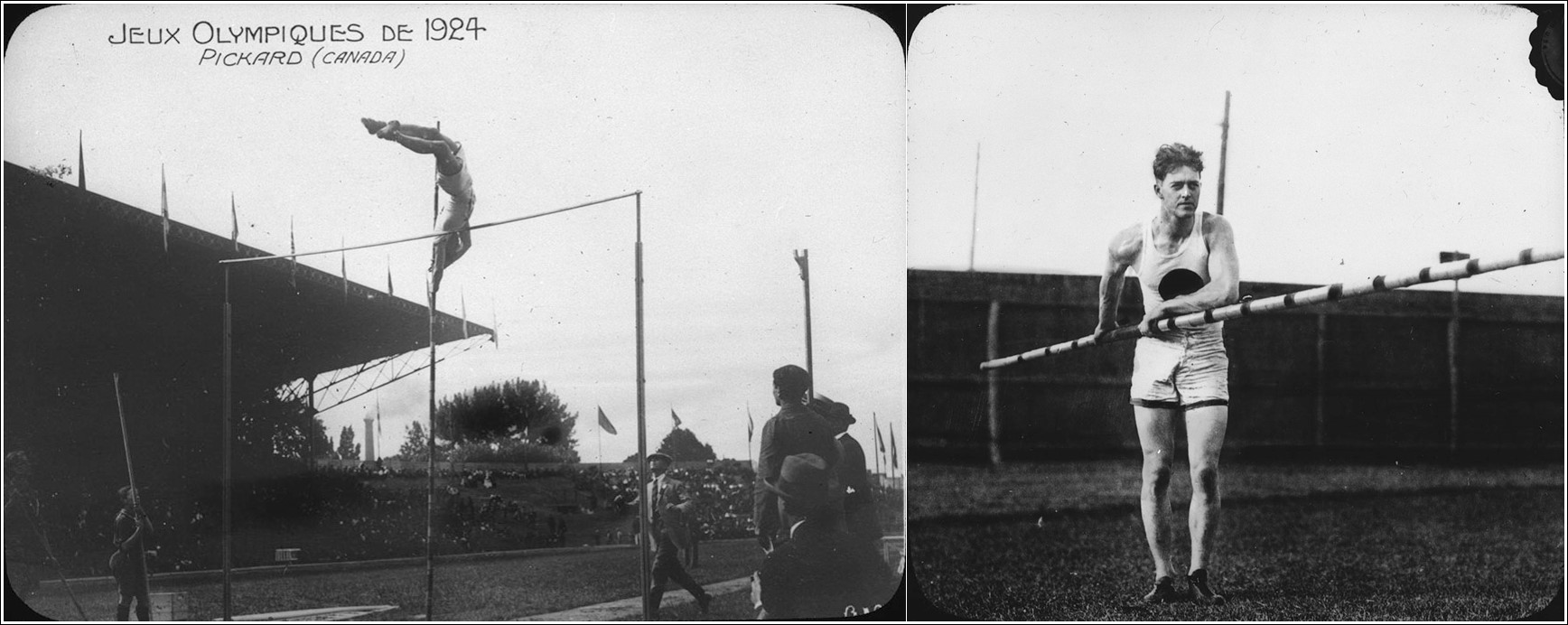
Another athlete who made his Olympic debut in 1924 is Victor Pickard, the pole vaulter and javelin thrower. Pickard represented Canada at two Olympic Games (1924 and 1928) and won a gold medal in pole vaulting at the British Empire Games in 1930. During his athletic career, Pickard’s highest jump at the Olympics was 3.45 m, but his personal best was 4.15 m. Today, the Canadian pole vault record stands at 6.00 m and the world pole vault record stands at 6.24 m.
While every Olympic Games is different, they always guarantee two things: excitement and excellence. Whether that’s through record-breaking performances, making a political statement or rallying around an athlete in need, the Olympics have got something for everyone. The Games have come to symbolize a lot more than just fair play, athleticism, and national identity. They’re a cultural moment. They bring people together in bars, in living rooms, and in schools. They’re history in the making and they’re just getting started.
Additional Resources
- Olympic Men’s Hockey 1920‐1972, Canada Hockey Hall of Fame Website
- Carved in granite: 125 years of Granite Club history, by Rod Austin and Ted Barris (OCLC 42275303)
- The Edmonton Grads, Heritage Minute
- From 1924 to 2024: Spotlight on the Paris Olympics, then and now
- 1924: Paris, France, CBC Sports
Sali Lafrenie is a Portfolio Archivist in the Private Archives Branch at Library and Archives Canada.